Can you keep your car if you file Chapter 7 bankruptcy? Yes, in many cases, you can keep your car when you file Chapter 7 bankruptcy. This is a common concern for individuals facing financial hardship. Fortunately, bankruptcy laws provide mechanisms for individuals to retain essential property, including vehicles, while discharging other debts. This detailed guide will explore how you can navigate the process of car ownership bankruptcy and successfully keep your car through Chapter 7 bankruptcy.
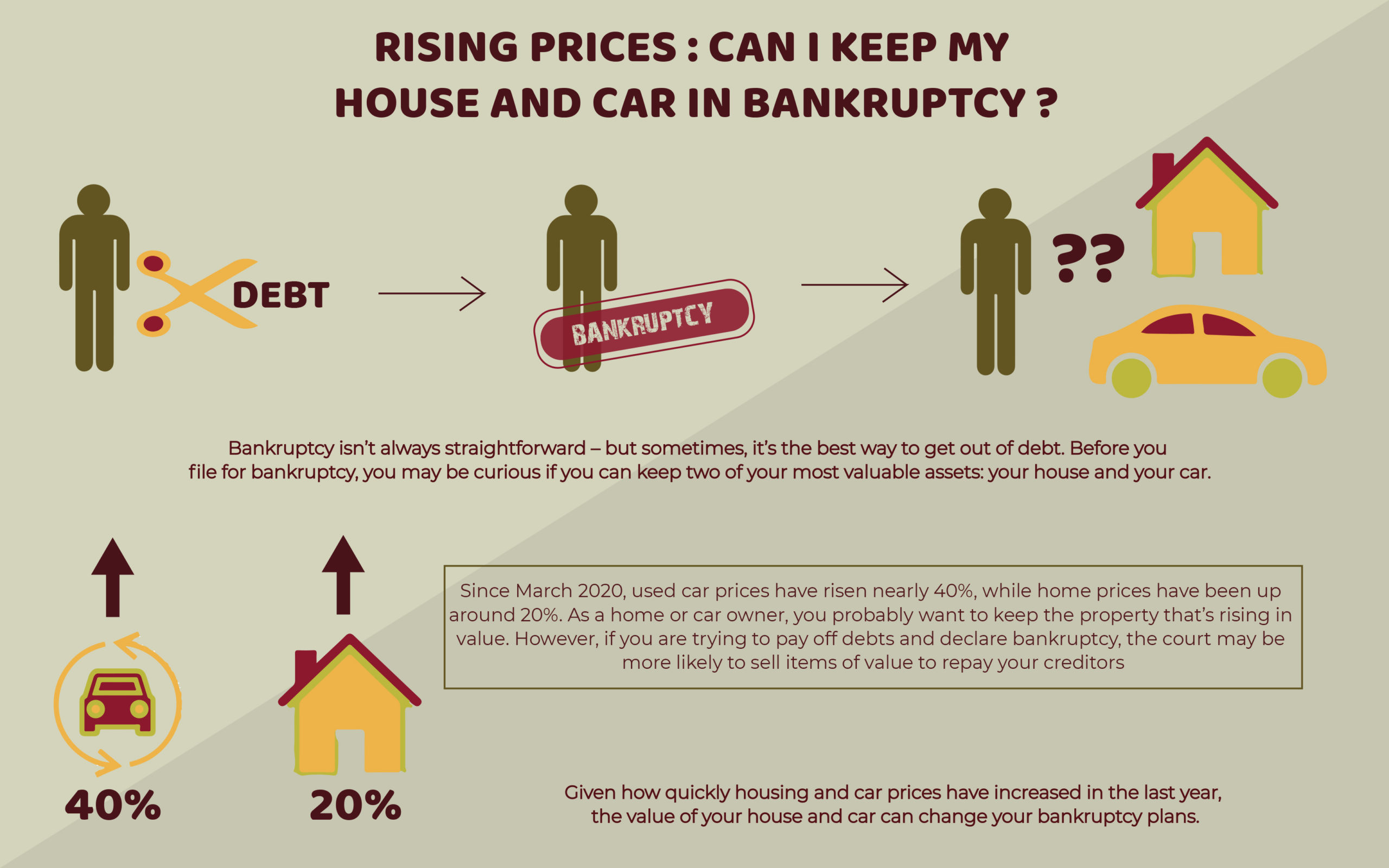
Image Source: www.therollinsfirm.com
Fathoming Vehicle Protection in Chapter 7
Chapter 7 bankruptcy, often called liquidation bankruptcy, involves selling non-exempt assets to pay creditors. However, not all assets are liquidated. The concept of exemptions is crucial here. Exemptions are legal protections that allow you to keep certain personal property. Your ability to keep your car hinges on its value relative to the available vehicle exemptions in your state.
The Role of Exemptions
Exemptions are the cornerstone of vehicle protection in Chapter 7. They are designed to ensure that individuals emerging from bankruptcy have essential items to re-establish themselves. These exemptions can be claimed at the federal level or at the state level, depending on where you live. Some states allow you to choose between federal and state exemptions, while others mandate the use of state exemptions only.
Federal Exemptions vs. State Exemptions
- Federal Exemptions: These are a set of exemptions available nationwide. They typically include a wildcard exemption that can be applied to any asset, including a car, and a specific exemption for a motor vehicle.
- State Exemptions: Each state has its own set of exemptions, which can vary significantly. Some states offer very generous vehicle exemptions, making it easier to keep a car, while others have more limited protections.
It is vital to research the specific exemption laws in your state. Your bankruptcy attorney will guide you through this process to ensure you claim the maximum exemptions available to you.
Calculating Your Car’s Equity
The key factor in determining whether you can keep your car is its auto equity in Chapter 7. Equity is the difference between your car’s current market value and the amount you owe on your car loan.
Equity = Current Market Value of Car – Outstanding Loan Balance
For example, if your car is worth $10,000 and you owe $5,000 on the loan, you have $5,000 in equity. If the total equity in your car is less than or equal to the applicable chapter 7 car exemption, you can typically keep the vehicle without owing any additional payment to the lender.
Factors Affecting Car Value
- Make and Model: Certain makes and models hold their value better than others.
- Age and Mileage: Older cars with high mileage generally have lower market values.
- Condition: The overall condition of the car, including mechanical and cosmetic aspects, significantly impacts its worth.
- Market Demand: Local market conditions can also influence a car’s value.
You can estimate your car’s value using online resources like Kelley Blue Book (KBB), Edmunds, or NADA Guides.
Strategies for Keeping Your Vehicle
If your car’s equity exceeds the available exemptions, or if you have a significant outstanding loan balance, there are specific strategies you can employ to keep your vehicle. These strategies often involve making arrangements with your lender.
Reaffirming Your Car Loan
One of the most common ways to keep your car when you have equity or a loan is to reaffirm your car loan. Reaffirming a debt means that you agree to continue making payments on that debt after your bankruptcy is discharged. When you reaffirm a car loan, you are essentially telling the court and the lender that you still want the car and are committed to paying the loan as originally agreed.
The Reaffirmation Process
- Agreement: You and the lender must agree to the reaffirmation. The lender is not obligated to allow reaffirmation if you are behind on payments.
- Court Approval: The reaffirmation agreement must be filed with the bankruptcy court. In most cases, if the debtor is represented by an attorney, the court will approve it. If the debtor is not represented by an attorney, the court will hold a hearing to ensure the reaffirmation does not impose an undue hardship on you and is in your best interest.
- Continuing Payments: After the court approves the reaffirmation, you continue making your regular car payments. The loan is removed from your bankruptcy discharge, meaning it will remain on your credit report and you are legally obligated to pay it.
Benefits of Reaffirming:
- Keeps Your Car: This is the primary benefit.
- Preserves Credit: By continuing payments, you can potentially improve your credit score over time.
- Avoids Repossession: You ensure the lender cannot repossess the vehicle for non-payment after the bankruptcy.
Considerations for Reaffirming:
- Financial Stability: You must be confident in your ability to make the payments going forward.
- Interest Rate: The interest rate on the loan will remain the same.
- Future Hardship: If you face financial difficulties again, you will still be responsible for the loan.
The Redemption Option
Another strategy, particularly if you want to own the car outright but cannot afford to reaffirm the loan, is redemption. In Chapter 7 bankruptcy, you have the option to “redeem” your vehicle. This means you pay the lender the current market value of the car, rather than the full amount owed on the loan.
How Redemption Works
- Payment: You must pay the lender the car’s present value in a lump sum. This can be paid with cash, through a personal loan, or by using savings.
- Lump Sum Requirement: The key challenge with redemption is the need for a lump-sum payment, which can be difficult for individuals filing bankruptcy.
- Lien Release: Once you pay the redeemed amount, the lender must release their lien on the vehicle, making you the full owner.
Benefits of Redemption:
- Lower Payment: You pay the actual value, not the outstanding loan balance, potentially saving money.
- Clear Title: You own the car outright with no further loan obligations.
Considerations for Redemption:
- Cash Availability: Requires immediate access to cash, which is often scarce for those filing bankruptcy.
- Lender Cooperation: While the law allows redemption, some lenders may try to complicate the process.
Keeping the Car “As Is”
In some situations, if your car is not worth much, and you owe more than it’s worth (negative equity), you might be able to keep it without reaffirming or redeeming. This is often referred to as keeping the car “as is.”
The “As Is” Scenario
- No Equity: If the car has no equity or negative equity (you owe more than it’s worth), and you are current on your payments, the trustee may not see it as an asset worth liquidating.
- No Reaffirmation: You don’t reaffirm the loan. This means the car loan will be discharged in bankruptcy.
- Lender Action: The lender can still repossess the car if you stop making payments after the bankruptcy. You are no longer personally liable for the debt, but the lender can still take the collateral (the car) if the loan is not paid.
Pros of Keeping “As Is”:
- No Immediate Payment Obligation: You don’t need to make a lump sum payment or formally reaffirm.
- Potential to Continue Driving: You may be able to continue driving the car as long as you make payments and the lender doesn’t act.
Cons of Keeping “As Is”:
- Risk of Repossession: If you miss payments, the lender can repossess the car.
- No Ownership Guarantee: You don’t have a guaranteed right to keep the car long-term.
- Credit Impact: The loan may still appear on your credit report, and continued payments might not be reported in a way that helps build credit.
Surrendering the Vehicle
While the goal is to keep your car, sometimes the most practical option is to surrender the car in Chapter 7. This means voluntarily giving the car back to the lender.
When Surrendering is Necessary
- No Equity and Behind on Payments: If you have no equity and are significantly behind on payments, surrendering might be the best way to avoid further penalties or collection actions.
- Affordability Issues: If you cannot afford the car payments, insurance, or maintenance, or if you cannot afford to reaffirm or redeem, surrendering may be the most responsible choice.
- Unfavorable Loan Terms: If you have a high-interest loan that makes it difficult to manage, surrendering and finding more affordable transportation might be a better long-term solution.
The Surrender Process
- Notification: Inform the lender and your bankruptcy trustee that you intend to surrender the vehicle.
- Return: Arrange for the car to be returned to the lender.
- Debt Discharge: The remaining balance on the loan after the car is sold at auction is typically discharged in your bankruptcy. However, if there is a “deficiency balance” (the sale price is less than what you owed), the lender may try to collect this from you if you reaffirmed the loan. If you did not reaffirm, the deficiency is usually discharged.
Benefits of Surrendering:
- Eliminates Debt: The loan balance is discharged, freeing you from that financial obligation.
- Avoids Further Costs: You stop incurring car payments, insurance, and maintenance costs.
- Focus on Other Debts: Allows you to focus financial resources on other obligations or essential needs.
Considerations for Surrendering:
- Loss of Transportation: This is the most significant drawback. You will need to find alternative transportation.
- Impact on Credit: While the debt is discharged, the repossession will negatively impact your credit score.
Crucial Steps for Automobile Chapter 7 Bankruptcy Success
Navigating the complexities of automobile chapter 7 bankruptcy requires careful planning and adherence to legal procedures. Here are essential steps to maximize your chances of keeping your car.
1. Consult a Bankruptcy Attorney
This is arguably the most critical step. A qualified bankruptcy attorney will:
- Assess Your Situation: They will evaluate your income, expenses, assets, and debts.
- Identify Exemptions: They will explain the federal and state exemptions available in your jurisdiction and help you choose the most advantageous ones.
- Advise on Strategy: They will guide you on whether reaffirmation, redemption, or another approach is best for your specific circumstances.
- File Necessary Documents: They will ensure all paperwork is filed correctly and on time with the court.
2. Gather Essential Documentation
Accurate and complete documentation is vital. You will need:
- Vehicle Information: Title, registration, purchase agreement.
- Loan Documents: All paperwork related to your car loan.
- Proof of Value: Recent estimates of your car’s market value.
- Proof of Insurance: Confirmation that your car is insured.
- Income and Expense Statements: Detailed records of your financial situation.
3. Understand Your State’s Specific Laws
As mentioned, state laws regarding exemptions vary significantly. For instance:
- Homestead States: Some states, like Florida and Texas, have very generous homestead exemptions that can sometimes be applied to personal property, including vehicles, via a wildcard exemption.
- Limited Exemptions: Other states may have lower exemption amounts for vehicles.
Your attorney will be knowledgeable about these nuances.
4. Attend the Meeting of Creditors (341 Meeting)
This mandatory meeting is where the bankruptcy trustee and any creditors can ask you questions under oath about your financial situation and the bankruptcy car asset. Your attorney will prepare you for this meeting.
5. Fulfill Reaffirmation or Redemption Requirements
If you choose to reaffirm or redeem your car, you must meticulously follow the court’s procedures and your lender’s requirements. Missing deadlines or failing to provide necessary documentation can jeopardize your ability to keep the vehicle.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What happens to my car loan if I don’t reaffirm it in Chapter 7?
If you don’t reaffirm your car loan and you have equity in the car exceeding your exemptions, the trustee may sell the car to pay creditors. If you have no equity and don’t reaffirm, the loan is discharged, but the lender can still repossess the car if you stop making payments.
Q2: Can I keep my car if I’m behind on payments when I file Chapter 7?
It’s more complicated. If you’re behind, the lender can usually repossess the car even after filing. To keep it, you generally need to catch up on missed payments in addition to reaffirming the loan or redeeming the vehicle. This is often done through a reaffirmation agreement or, in some rare cases, by negotiating with the lender.
Q3: How is the car’s value determined in Chapter 7?
The car’s value is typically its current wholesale or retail market value, depending on how it’s being evaluated. You can get estimates from sources like Kelley Blue Book (KBB), Edmunds, or NADA Guides. The bankruptcy trustee may also have the vehicle appraised if there’s a dispute about its value.
Q4: What if my car is jointly owned?
If your car is jointly owned with a spouse, both individuals’ financial situations and exemptions come into play. You’ll need to discuss this specific scenario with your bankruptcy attorney, as the laws for jointly owned property can be complex.
Q5: Does bankruptcy affect my ability to get a car loan in the future?
Yes, bankruptcy will likely impact your ability to get a car loan immediately after discharge. However, it’s a temporary effect. By rebuilding your credit responsibly after bankruptcy, you can qualify for car loans again over time.
Final Thoughts on Chapter 7 Asset Protection
Successfully keeping your car during Chapter 7 bankruptcy is achievable for many. It requires a thorough understanding of chapter 7 car exemption laws, an accurate assessment of your auto equity in Chapter 7, and strategic decision-making regarding reaffirmation, redemption, or even surrender. By seeking professional legal guidance and diligently preparing your case, you can protect this vital asset and navigate your bankruptcy with greater peace of mind. Remember, the goal of bankruptcy is to provide a fresh start, and this often includes retaining essential transportation to rebuild your life.